38 are treasury bills zero coupon bonds
› articles › investingAdvantages and Risks of Zero Coupon Treasury Bonds - Investopedia Jan 31, 2022 · Zero-coupon U.S. Treasury bonds have a poor risk-return profile when held alone. Long-dated zero-coupon Treasury bonds are more volatile than the stock market, but they offer the lower long-run ... What Are Treasury Bills (T-Bills) and How Do They Work? - Investopedia T-bills are zero-coupon bonds that are usually sold at a discount and the difference between the purchase price and the par amount is your accrued interest. How Can I Buy a Treasury Bill? U.S....
› treasury-bonds-4689773Investing in Treasury Bonds - Investopedia Dec 30, 2021 · Treasury Bonds vs. Treasury Notes vs. Treasury Bills. By. Nick Lioudis. Updated Mar 29, 2022. ... Advantages and Risks of Zero Coupon Treasury Bonds. By. Lisa Smith. Updated Jan 31, 2022.

Are treasury bills zero coupon bonds
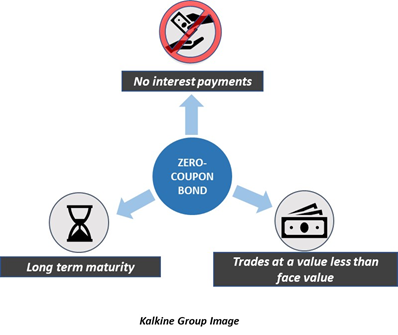
Zero Coupon Bond | Investor.gov Zero Coupon Bond. Zero coupon bonds are bonds that do not pay interest during the life of the bonds. Instead, investors buy zero coupon bonds at a deep discount from their face value, which is the amount the investor will receive when the bond "matures" or comes due. The maturity dates on zero coupon bonds are usually long-term—many don't mature for ten, fifteen, or more years. Treasury Coupon Issues and Corporate Bond Yield Curves Corporate Bond Yield Curve Papers and Data. Learn about the corporate bond yield curve, and how it relates to the Pension Protection Act, by downloading these papers. Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade (TTB) Bureau of Engraving and Printing (BEP) Bureau of the Fiscal Service (BFS) Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) Zero-coupon bond - Wikipedia A zero coupon bond (also discount bond or deep discount bond) is a bond in which the face value is repaid at the time of maturity. [1] Unlike regular bonds, it does not make periodic interest payments or have so-called coupons, hence the term zero-coupon bond. When the bond reaches maturity, its investor receives its par (or face) value.
Are treasury bills zero coupon bonds. Government Securities Market in India – A Primer Treasury bills are zero coupon securities and pay no interest. Instead, they are issued at a discount and redeemed at the face value at maturity. What is Treasury Bill (T-bill)? - Indian Economy Treasury bills are presently issued in three maturities, namely, 91 day, 182 day and 364 day. Treasury bills are zero coupon securities and pay no interest. Rather, they are issued at a discount (at a reduced amount) and redeemed (given back money) at the face value at maturity. Treasury Bills vs Bonds | Top 5 Differences (with Infographics) T-bills do not pay any coupon. They are floated as a zero-coupon bond Zero-coupon Bond In contrast to a typical coupon-bearing bond, a zero-coupon bond (also known as a Pure Discount Bond or Accrual Bond) is a bond that is issued at a discount to its par value and does not pay periodic interest. In other words, the annual implied interest payment is included into the face value of the bond, which is paid at maturity. What's the difference between a zero-coupon bond and a Treasury ... T-bills do not pay any coupon. They are floated as a zero-coupon bond to the investors, they are issued at discounts, and the investors receive the face value ...
Understanding Pricing and Interest Rates — TreasuryDirect The formula shows that the bill sells for $999.27, giving you a discount of $0.73. Bonds and Notes. Bonds are long-term securities that mature in 20 or 30 years. Notes are relatively short or medium-term securities that mature in 2, 3, 5, 7, or 10 years. Both bonds and notes pay interest every six months. Understanding Zero Coupon Bonds - Part One - The Balance Zero coupon bonds generally come in maturities from one to 40 years. The U.S. Treasury issues range from six months to 30 years and are the most popular ones, along with municipalities and corporations. 1. Here are some general characteristics of zero coupon bonds: You must pay tax on interest annually even though you don't receive it until ... What's the difference between a zero-coupon bond and a Treasury bill ... Answer (1 of 2): T-bills are also called as zero coupon bond, which is issued at discount. T bills are short term instruments issued within one year. 91 days, 182 days, 364 days are the examples of maturity period. T-bills are issued by goverment of any country. One point to remember Bonds can ... Yield Curves for Zero-Coupon Bonds - Bank of Canada These files contain daily yields curves for zero-coupon bonds, generated using pricing data for Government of Canada bonds and treasury bills. Each row is a single zero-coupon yield curve, with terms to maturity ranging from 0.25 years (column 1) to 30.00 years (column 120). The data are expressed as decimals (e.g. 0.0500 = 5.00% yield). A ...
The One-Minute Guide to Zero Coupon Bonds | FINRA.org Instead of getting interest payments, with a zero you buy the bond at a discount from the face value of the bond, and are paid the face amount when the bond matures. For example, you might pay $3,500 to purchase a 20-year zero-coupon bond with a face value of $10,000. After 20 years, the issuer of the bond pays you $10,000. A guide to US Treasuries Separate Trading of Registered Interest and Principal of Securities (STRIPS): Treasury STRIPS, also known as zero-coupon Treasuries, let investors hold and trade the interest and principal of certain T-notes and bonds as separate securities. scripbox.com › pf › treasury-billsTreasury Bills - Meaning, Types, Yield Calculation & How to Buy? Sep 10, 2020 · Treasury bills are zero-coupon bonds, i.e. no interest is paid on them to investors. They are issued at a discount and redeemed at face value. Therefore, the returns earned by investors in T-bills remains fixed throughout the bond tenure irrespective of the economic condition of the country. Can you lose money on Treasury notes? | Note Brokering Treasury bills are not like coupon bonds that pay interest in accruals. What are Treasury bills example? Treasury bills are zero-coupon securities and do not pay interest. They are issued at a discount and are redeemed at face value at maturity. For example, a 91-day treasury bill of Rs. 100 / - (nominal value) can be issued for example Rs.
Zero-Coupon Bonds (ZCB) - ICICI Prudential Mutual Fund Zero-Coupon Bonds (ZCB). Mutual fund investments are subject to market risks, read all scheme related documents carefully. Zero-coupon Bond is a type of ...
Treasury bills are also known as Zero Coupon Bonds that ... - Toppr Treasury bills are also known as Zero Coupon Bonds that are available for a minimum of and in multiples thereof. A treasury bill is basically an instrument ...
› us-treasury-bondsUS Treasury Bonds - Fidelity Other Treasury securities, such as Treasury bills (which have maturities of one year or less) or zero-coupon bonds, do not pay a regular coupon. Instead, they are sold at a discount to their face (or par) value; investors receive the full face value at maturity. These securities are known as Original Issue Discount (OID) bonds, since the difference between the discounted price at issuance and the face value at maturity represents the total interest paid in one lump sum.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › TED_spreadTED spread - Wikipedia The TED spread is an indicator of perceived credit risk in the general economy, since T-bills are considered risk-free while LIBOR reflects the credit risk of lending to commercial banks. An increase in the TED spread is a sign that lenders believe the risk of default on interbank loans (also known as counterparty risk ) is increasing.
United States Treasury security - Wikipedia Treasury bills (T-bills) are zero-coupon bonds that mature in one year or less. They are bought at a discount of the par value and, instead of paying a coupon interest, are eventually redeemed at that par value to create a positive yield to maturity.. Regular T-bills are commonly issued with maturity dates of 4, 8, 13, 26 and 52 weeks, each of these approximating a different number of months.
What Is a Zero-Coupon Bond? Definition, Advantages, Risks Jul 28, 2022 ... A zero-coupon bond doesn't pay periodic interest, but instead sells at a deep discount, paying its full face value at maturity.
Treasury Bills — TreasuryDirect Treasury Bills. Treasury bills, or T-bills, are sold in terms ranging from a few days to 52 weeks. Bills are typically sold at a discount from the par amount (par amount is also called face value); rarely, they have sold at a price equal to the par amount. When a bill matures, you are paid its par amount. If the par amount is greater than the ...
Zero Coupon Bonds- Taxability Under Income Tax Act, 1961 - TaxWink Zero Coupon Bonds assures a fixed maturity amount after a certain period. Therefore, the investors who have want to get a fixed return in future with less market risk should go for these bonds. Even if you are an aggressive investor and always hunting for good stocks, you may still invest in these bonds to balance your portfolio.
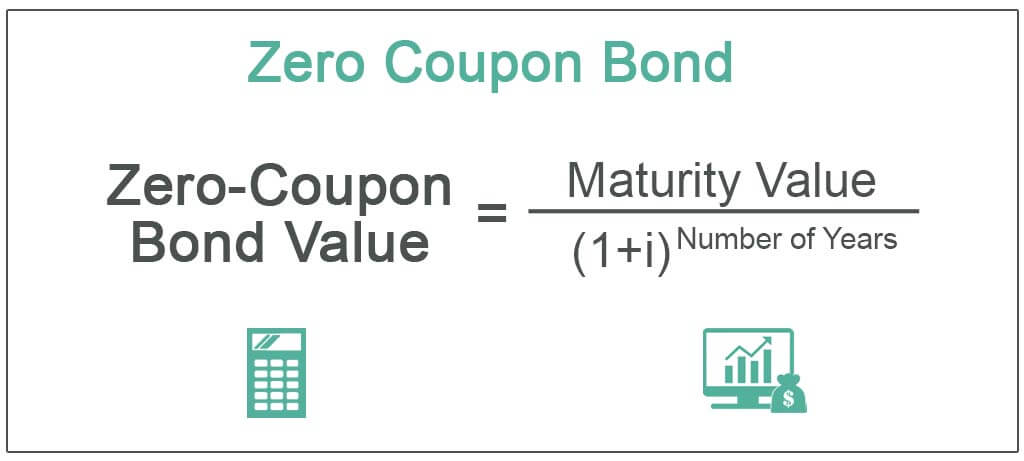
Zero-Coupon Bond - Definition, How It Works, Formula It is also called a pure discount bond or deep discount bond. U.S. Treasury bills are an example of a zero-coupon bond. Summary A zero-coupon bond is a bond that pays no interest. The bond trades at a discount to its face value. Reinvestment risk is not relevant for zero-coupon bonds, but interest rate risk is relevant for the bonds.
US Treasury Securities - Taxable Bonds | Raymond James STRIPS, or Separate Trading of Registered Interest and Principal of Securities, are a special kind of Treasury bond created by a process called "coupon stripping.". Principal and interest are separated and sold individually as zero-coupon bonds at a discount from their par value. For example, stripping of a 15-year bond will result in 30 ...
Treasury Coupon Issues | U.S. Department of the Treasury Treasury Coupon Issues. The Yield Curve for Treasury Nominal Coupon Issues (TNC yield curve) is derived from Treasury nominal notes and bonds. The Yield Curve for Treasury Real Coupon Issues (TRC yield curve) is derived from Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS). The Treasury Breakeven Inflation Curve (TBI curve) is derived from the TNC and TRC yield curves combined.
Treasury Bills - Guide to Understanding How T-Bills Work T-bills, T-notes, and T-bonds are fixed-income investments issued by the US Department of the Treasury when the government needs to borrow money. They are all commonly referred to as "Treasuries." T-Bills Treasury bills have a maturity of one year or less, and they do not pay interest before the expiry of the maturity period.
Should You Buy Treasuries? - Forbes The shortest U.S. bonds, T-bills, are sold at auction at a discount to the face value (par). Bills mature at par and don't pay interest. Treasury notes and bonds pay interest every six months.
Treasury Bills vs. Bonds: What's the Difference? - SmartAsset Treasury Bills vs. Savings Bonds. Another common type of bond is the U.S. savings bond. Like T-bills and T-bonds, savings bonds are issued by the Treasury Department to help fund government operations, making them reliable but not lucrative investments. However, unlike T-bills and T-bonds, savings bonds cannot be bought and sold on secondary ...
Treasury Bills vs Bonds | Top 5 Best Differences (With Infographics) Some of the key bonds are Municipal bonds, Governments bonds, corporate bonds, Zero Coupons bonds, etc. Bonds also called fixed-income instruments. Example: Let's say Smith purchased a government bond from the government for a worth of INR 10,000 and the term of the bond is 10 years, with an interest rate of 4.75%.
Treasury Bills (T-Bills) - Meaning, Examples, Calculations - WallStreetMojo Treasury bills are a type of zero-coupon security where the central government borrows funds from the individual for a period of 364 days or less. In return, the investors receive interest. These money market instruments provide a return on investment at once, and there is no provision for periodic returns.
Zero-Coupon Bond: What are Zero-Coupon Bonds? - Wall Street Prep Zero-coupon bonds are often perceived as long-term investments, although one of the most common examples is a "T-Bill," a short-term investment. U.S. Treasury Bills (or T-Bills) are short-term zero-coupon bonds (< 1 year) issued by the U.S. government. Learn More → Zero Coupon Bond (SEC) Zero-Coupon Bond Price Formula
groww.in › p › treasury-billsTreasury Bills - Types, Features and Advantages of ... - Groww Limitations of Treasury Bill. The primary disadvantage of government treasury securities is that they are known to generate relatively lower returns when compared to standard stock market investment tools. Treasury bills are zero-coupon securities, issued at a discount to investors. Hence, total returns generated by such instruments remain constant through the tenure of bond, irrespective of economic conditions and business cycle fluctuations.
coursehelponline.comCourse Help Online - Have your academic paper written by a ... 100% money-back guarantee. With our money back guarantee, our customers have the right to request and get a refund at any stage of their order in case something goes wrong.
Zero-coupon bond - Wikipedia A zero coupon bond (also discount bond or deep discount bond) is a bond in which the face value is repaid at the time of maturity. [1] Unlike regular bonds, it does not make periodic interest payments or have so-called coupons, hence the term zero-coupon bond. When the bond reaches maturity, its investor receives its par (or face) value.
Treasury Coupon Issues and Corporate Bond Yield Curves Corporate Bond Yield Curve Papers and Data. Learn about the corporate bond yield curve, and how it relates to the Pension Protection Act, by downloading these papers. Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade (TTB) Bureau of Engraving and Printing (BEP) Bureau of the Fiscal Service (BFS) Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN)
Zero Coupon Bond | Investor.gov Zero Coupon Bond. Zero coupon bonds are bonds that do not pay interest during the life of the bonds. Instead, investors buy zero coupon bonds at a deep discount from their face value, which is the amount the investor will receive when the bond "matures" or comes due. The maturity dates on zero coupon bonds are usually long-term—many don't mature for ten, fifteen, or more years.
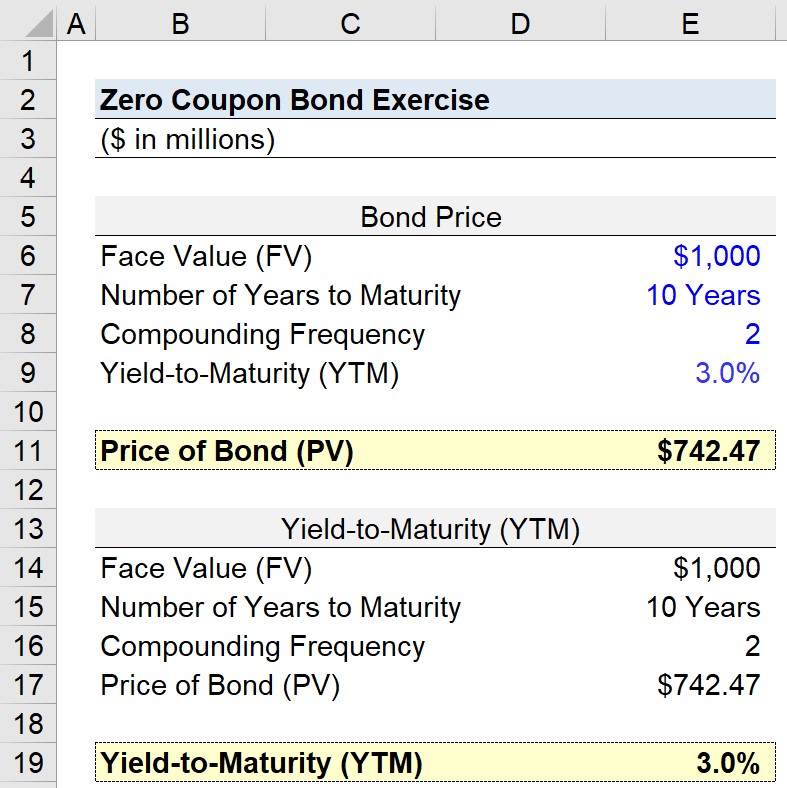


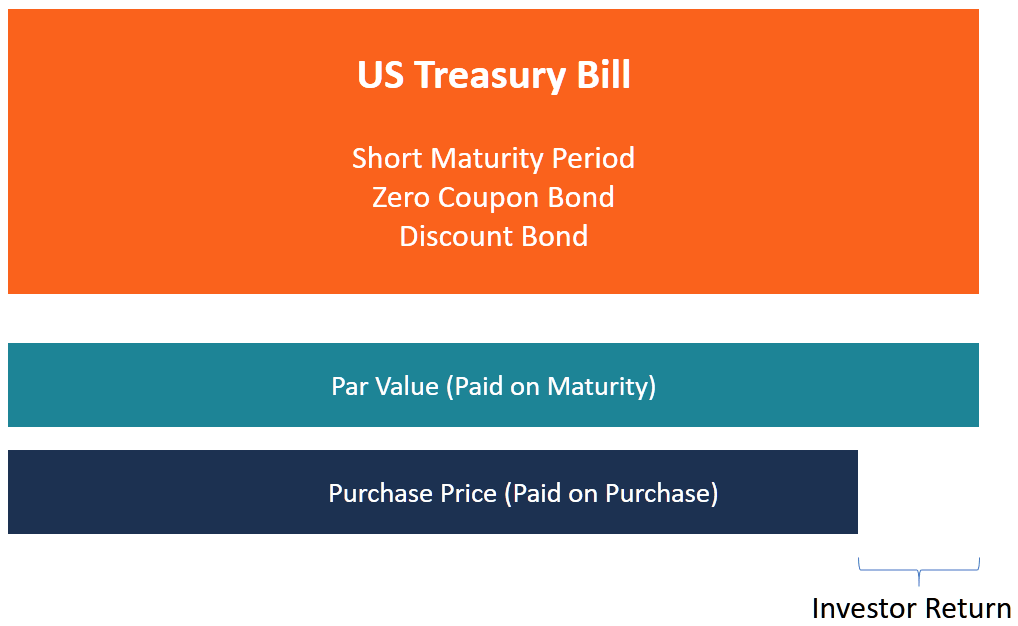
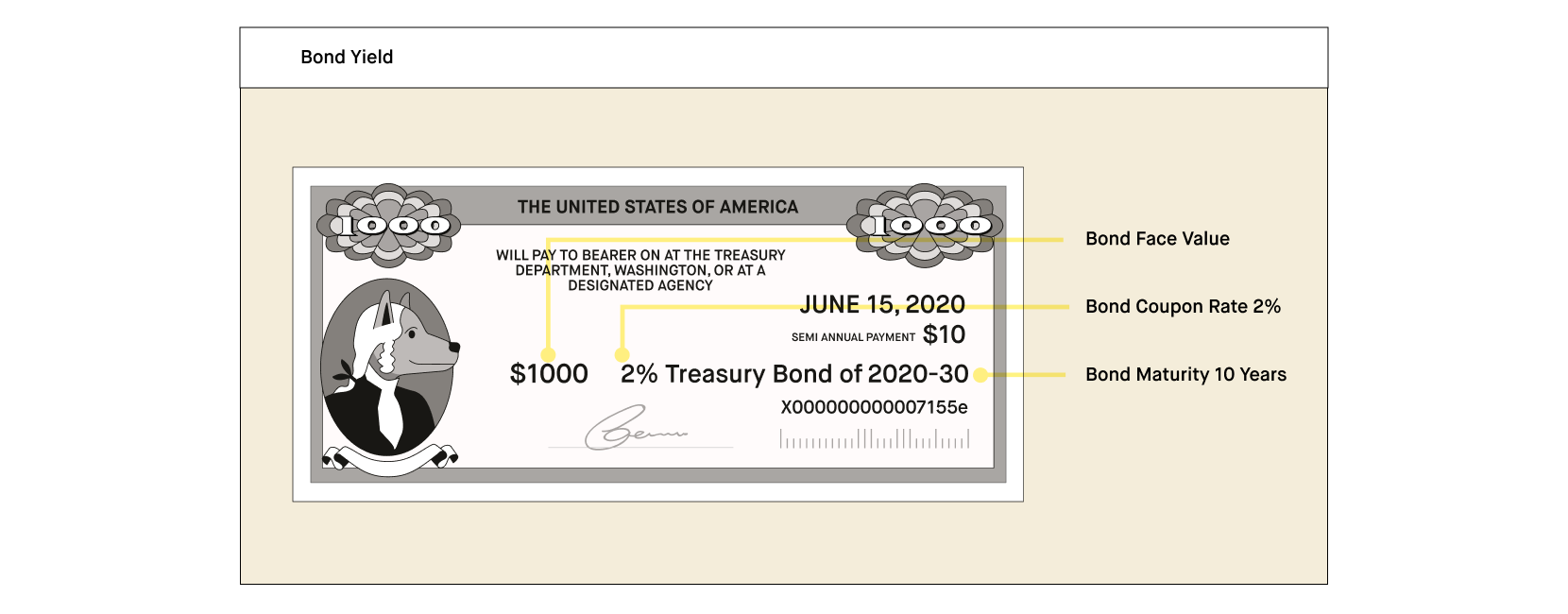

/zero-couponbond_final-a6ec3618516a49c9a3654a1c79c9b681.png)


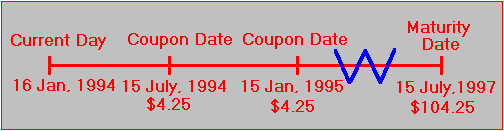


/-1000-denomination-us-savings-bonds-172745598-cdf4a528ed824cc58b81f0531660e9c9.jpg)









Post a Comment for "38 are treasury bills zero coupon bonds"